![]()
I BACK I RETURN I NEXT I BOTTOM I SUMMARY I
![]()
Nervous system in fish åà×¾ÀÇ ãêÌèͧ
|
|
|
|
|
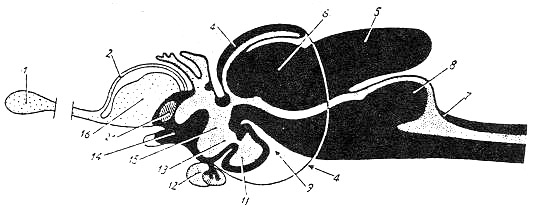
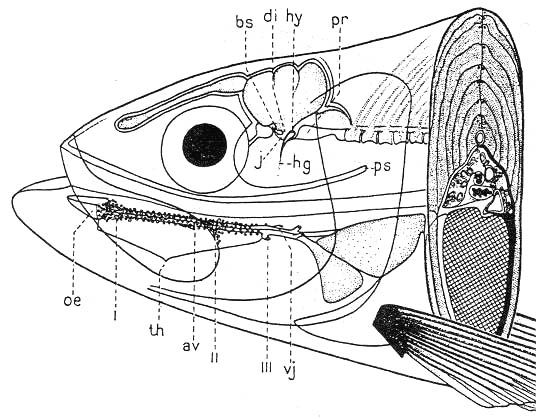
| I: Olfactory nerve, II: Optic nerve, 1: Olfactory bulb, 2: Telencephalon, 3: Mesencepahlon, 4: Metencephalon, 5: Myelencephalon, 6: Inferior lobe of diencephalon | |||
1. Central nervous system ñéõÒãêÌèͧ
|
|
|
|
|
1:Olfactpry bulb, 2:Telencephalon, 3.Epiphysis, 4: Mesencephalon, 5:Metencephalon, 6:Valvula cerebelli, 7:Myelencephalon, 8:Impar lobus, 9:Plica ventralis, 11:Saccus vasculosus, 12:Hypophysis, 13:Infundibulum, 14:Optic chiasma, 15:Diencephalon, 16:Basal ganglion and pallium(teleostei), 21:Commissura rostralis |

1) Brain Òà
--- a. Protencephalon(Prosencephalon)
--- Forebrain or cerebrum
--- Telencephalon\ Diencephalon
|
|
|
|
b. Deuterencephalon
--- Midbrain
--- Mesencephalon
c. Tritencephalon
--- Rhombencephalon or hindbrain
--- Myelencephalon
--- Medulla oblongata
--- Metencephalon
--- The most conspicuous part of which is the cerebellum
--- Cerebellum\ Pons
(1) Rhombencephalon(Tritencephalon\ Hindbrain)
--- No definite border from the spinal cord(medulla spinalis)
--- The passage through the foramen magnum of the skull
--- The shape of rhombencephalon
--- Strongly influenced by the organs of the stato-aucoustic apparatus
a. Myelencephalon (Medulla oblongata¡¬Hindbrin)
--- A transitional zone between the spinal cord and brain
Origins of cranial nerves below cranial nerve III (Oculomotor nerve)
|
|
|
|
|
|
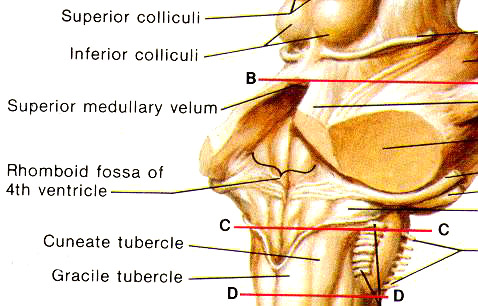
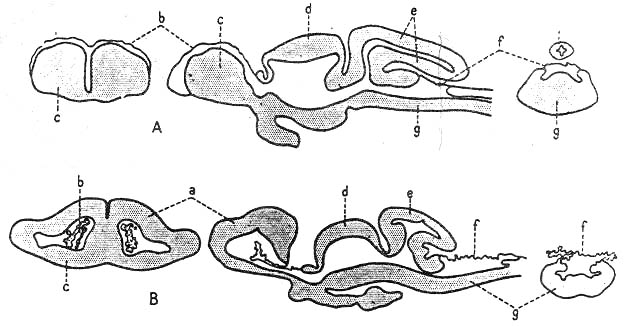
(a) Rhomboid fossa
--- Pronounced enlargement of central canal
--- A part of the 4th ventricle
--- From this, lateral recesssus
--- The rhombic shape
--- Most clearly apparent in the embryo
--- Later modified when the cerebellum develops
--- Variation in shape depending on the nucleus region
(b) Posterior velum(Velum posticum)
--- A single layered epithelium of the central canal
<--- Ependymal lining with cilia
---> Circulation of CSF
--- Closing-off the fossa rhomboidea of the central canal
--- Strongly folded epithelium in the elasmobranchii
--- Less extensive, less folded in the teleostei
|
|
|
|
(c) Posterior choroidal membrane(f)
--- Tela choroidea posterior
--- A large blood vessel plexus
--- Located in the folds of the velum
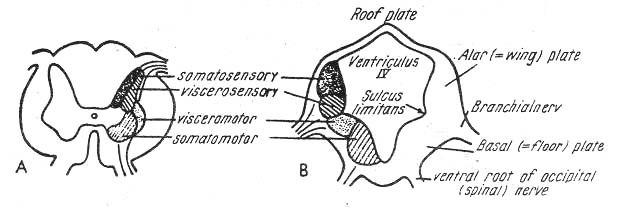
# Rhombencephalic sensory and motoric zones
|
|
|
|
Alar plate(Sensory zone)
--- a. Somatosensory zone
Sulcus intermedius dorsalis
b. Viscerosensory zone
Sulcus limitans internus
Basal plate(Motoric zone)
--- a. Viscero motoric zone
Sulcus intermedius ventralis
b. Somatomotoric zone
Sulcus medianus
b. Metencephalon
|
|
|
|
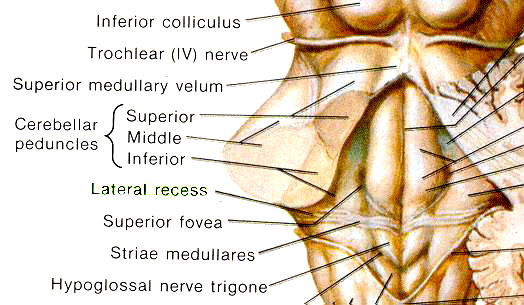
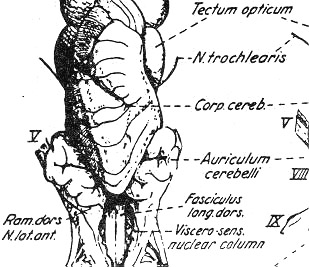
--- The cerebellum
---> A dorsal part
The main part of metencephalon
The pons
---> A ventral part
Rostral end of the rhombencephalon
Fusion of alar plate
---> Base of metencephalon
--- No well-defined border between the metencephalon and myelencephalon
--- Rhombomesencephalic fissure
--- Precise border between cerebellum and mesencephalon
--- Base of it
--- trochlear nerves (IV)
--- Crossing of trochlear nerves
No precise border between mesencephalon and metencephalon
--- Well-developed cerebellum
---> Covering of the rhomboid fossa
a. Superficial molecularis (A fibrous layer)
b. Purkinje's cell layer
c. Deeper granularis (Perikarya)
--- Lined by ependyma
--- A component of both the area statica and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
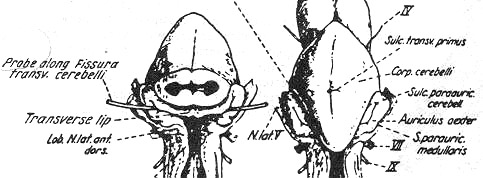
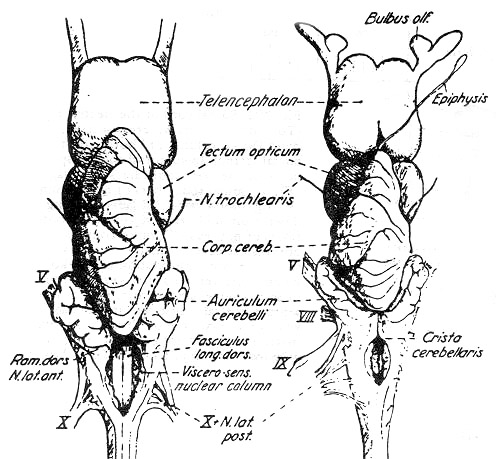
¨ç Auriculum cerebelli on each side of cerebellum
--- Elasmobranchii
--- Formed by lateral wall of myelencephalon
¨è Trasnverse lip in elasmobranchii
|
|
|
|
--- Arcus cerebellaris in teleostei
Archicerebellum(Vestibulocerebellum) in mammals
--- Connecting part between both sides of auricula
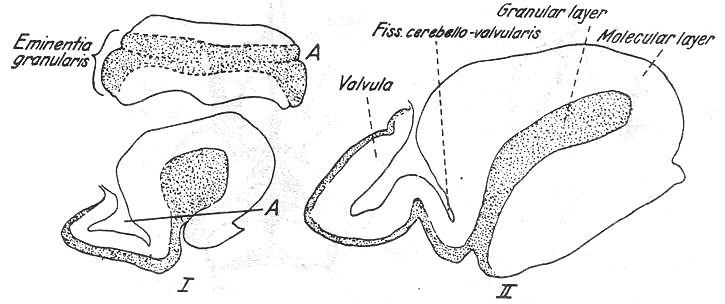
¨é Eminentia granularis in teleostei
1) Elasmobranchian cerebellum
|
|
|
|
--- Cerebellar body(Corpus cerebelli)
--- (a) Anterior lobe
(b) Posterior lobe
--- Median furrow, a continuation of the sulcus medianus of the spinal cord
--- Sulcus transversus primus
--- No valvula cerebelli
# Sulcus marginalis --- Marginal lobe
Median furrow ------- Median ridge
Fissura postica ----- Lobus posticus
|
|
|
|
2) Teleostean cerebellum
(1) Corpus cerebelli
a. Head portion
--- Above the velum posticum/ therefore above the rhomboid fossa
b. Neck portion
--- The connection to the myelencephalon
--- A process of 4th ventricle
--- Inner layer of the granulosa and outer layer of molecularis
|
|
|
|
--- Lateral growth of the granulosa
---> Emientia granularis
<--- Enclosing auricular parts(partes auriculares)
--- Only in teleostei
# Auricular parts(Partes auriculares)
--- Separated auricle in elasmobranchii
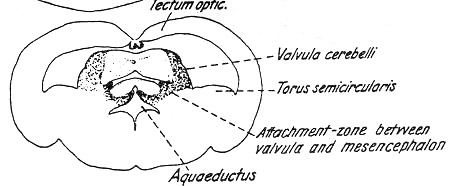
(2) Valvula cerebelli
--- A tongue-like protrusion into the ventricle of mesencephalon
--- Originated from fissura rhombencephalica
--- Absent in elasmobranchii
|
|
|
--- A number of lobes
(a) A lobus medialis valvulae (Medioventralis valvulae)
(b) 2 lateral lobes(lobi lateralis or laterodorsalis)
--- Molecular layer lining of invaginated internal cavity of ventricle (Cavum crani)
Epithelial lining by velum anticum (= anterius) or tela mesencephalica
Entire valvula enclosed inside the mesencephalon
--- Fissura postrema in elasmobranchii
--- The most posterior primary trqansverse fissure
--- Also called sulcus paraauricularis
--- Ventral molecular layer\ Posterior cerebellar sulcus(Transverse sulcus)
c. Mesencephalon
|
|
|
|
--- In front of metencephalon\ In back of diencephalon
--- The most prominent portion of the teleostean brain
a) The floor of mesencephalon
|
|
|
|
--- Subtectum
--- The floor of mesencephalon
--- Fusion with the rhombencephalon
--- Inner wall of subtectum
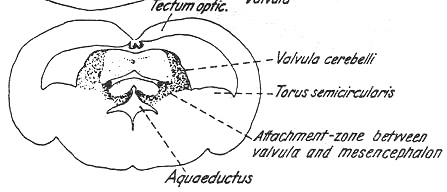
(a) Tori semicircularis
(b) Sulcus limitans(Alar\ Basal plates)
--- Nucleus of oculomotor nerve(III)
Fasciculus longitudinalis posterior
Sulcus interencephalicus
--- Located at the border with rhombencephalon
Commissura ansulata
--- Outer ventral surface of mesencephalon
Interpeduncular ganglion(Ganglion (Corpus) interpeduncularae)
--- Not always externally visible
--- Oculomotor nerves(III) of both sides
|
|
|
2) The roof of mesencephalon
--- Optic tectum(Tectum opticum)
--- All fibres from the optic nerve
--- Formation of their centers (Main optic center)
--- All fish\ Other vertebrates
--- 2 dome-like hills (Right and left optic lobes)
--- Floor of lobes
--- Fomation of tela mesencephalica (A thin epithelial layer)
--- After complete development of valvular cerebelli
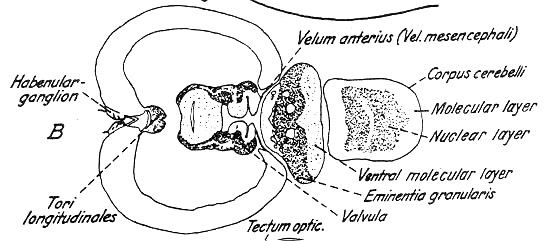
--- Tori longitudinales
--- Adjustment of body position in space
--- Optic and gravitational sensations
--- Bulging towards the ventricle from the medial edges of the lobes
--- Rostrally thicker
Torus semicircularis
--- Basal portion of alar plate
--- # Dorsal portion of that
--- Optic tectum(Tectum opticum)
--- A curved bulge located at the base of each optic lobe
Lying against the inner dorsal surface of the base of the
mesencephalon
Surrounding valvular cerebelli
3) Ventricles of mesencephalon
|
|
|
--- Very wide in teleostei since it comprises the valvula cerebelli
--- Mesencephalic ventricle(Ventriculus mesencephali)
--- Very wide lumen
--- Narrow Sylvian aqueduct in mammals
--- Large valvular cerebelli
|
|
|
|
--- 2 flat-crevice-like openings
--- ¨ç Recessus tecti (Dorsal one)
--- A closed caudal ending
¨è Cerebral aqueduct(Aqueductus cerebri (Ventral one))
--- Connected to the ventricles of diencephalon and myelencephalon
d. Diencephalon
--- Pituitary
Epiphysis (= pineal- and parietal organ)
Saccus vasculosus
<=== Endocrine functions
|
|
|
|
--- No precise borders of the diencephalon
¨ç Border from the telencephalon
--- Paraphysis and velum transversum(as anterio-dorsal border)
Optic recess(as anterior-ventral border)
# Velum transversum
--- Epithelial invagination projecting into the 3rd ventricle
¨è Border from the mesencephalon
--- Posterior commissure(Posterior dorsal border)
Mammillary body(Posterior ventral border)
1) Roof of the diencephalon
--- Epithalamus
Side walls of that
--- Thalamus
Floor of that
--- Hypothalamus in infundibular region
2) Paraphysis
|
|
|
|
--- Thin-walled, tub-like cone
--- Rostral evagination from the roof of the diencephalon
--- No known function
Velum transversum
--- Invagination into ventricle behind paraphysis
--- Thin-walled epithelial structure
--- A plexus choroideus located
Saccus dorsalis
--- Further caudal to velum transversum
3) Parietal (Parapineal) or pineal organs
--- Dorsal to the habenular ganglion
On the epiphygeal padding
--- Clearest in the agnatha
--- Regressed in all of the gnathostomes
Light-sensitive in pineal organ in petromyzon
4) Epiphysis
|
|
|
|
--- Developing from the pineal organ
--- Anterior to epiphysis
---> Parietal organ
# Parietal organ and pineal organs (pineal body)
--- Disappearance of parietal organ
# Habenular ganglia
--- Nervous interconnection
5) Posterior commissure
--- The posteriormost portion of the epithalamus
--- ie., situated directly in front of the mesencephalon
Epithalamus
Thalamus
--- The lateral wall of the diencephalon/ Being protruded into the 3rd ventricle
--- Dorsal border
--- Sulcus subhabenularis
Ventral border
--- Sulcus limitans (Sulcus ventralis)
Caudal border
--- Recessus metathalamicus/ Eminentia commissuralis/ Corpus postcommissurale
--- Division of thalamus by sulcus medius
--- ¨ç Caudo-dorsal portion
¨è Rostro-ventral portion
Hypothalamus
--- Dominant part of the diencephalon
Subdivision by a large number of furrows or sulcus and process of 3rd ventricle
a. Lateral lobes (inferior lobes\ right and left ones)
--- Lateral protrusion from the infundibular region
--- Occupying entire lateral wall
--- Egg-, kidney- or bean-shaped
b. Mammillary body
--- By mammillary sulcus
--- Location of mammillary ganglion
c. Saccus vasculosus
--- At the caudal fusion of both of the mammillary lobes
# Not being paired in teleostei
d. Posterior recess
--- Teleosts
--- Usually a small, well-defined protrusion
--- Between the saccus and the raphe between the right and left lobi inferiores and
mammillares
e. Medial lobe
--- Between the lobi inferiores (laterales)
--- Attached to hypophysis (pituitary gland)
f. Pituitary
--- Pituitary stalk
--- Infundibular recess
# Solid stalk in the elasmobranchii
g. Lateral optic recess
--- In the ventro-lateral wall of the 3rd ventricle
--- Situated at the level of the crossing of the optic nerves
h. Chiasma opticum (Crossing of optic nerves)
--- Ventral to the lamina terminalis
--- Structure of the 3rd ventricle
--- Recessus
--- Infundibulum\ Mammillary body\ Parapophysis\ Epiphysis\ Saccus vasculosus
--- Path into the 4th ventricle
--- Ventral to the posterior commissure
--- Subcommissural organ
--- Secretion of the thread of Reissner
--- 4th ventricle <---> Central canal of the spinal cord
e. Telencephalon
--- Olfactory brain (rhinencephalon) in fish
--- Olfactory organ
----------------> Telencephalon
Afferent nerves
(Olfactory nerve)
|
|
|
|
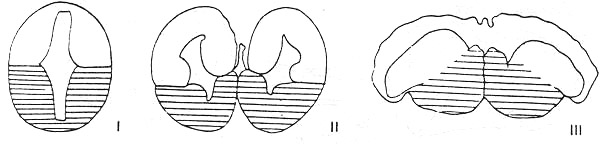
--- Types of telencephalon in fish
--- a. Elasmobranchii\ Dipnoi
b. Teleostei
c. Chondrostei (intermediate type)
# The 1st\ 2nd ventricles in the 2 separate ventricular lumen of the telencephalon divided
by the longitudinal dorsal furrow
--- Elasmobranchii/ Dipnoi
--- Teleostean telencephalic ventricle
--- The 1st\ 2nd ventricles
---> Common ventricle
Fusion ---> Intercephalic sulcus
(Between copora striata)
--- Corpus striatum
--- Determinator of telencephalic shape
--- Basal portion of the telencephalon
Corresponding to the basal plate of the spinal cord
Corpus epistriatium (Basal pallium)
--- Corresponding to the alar plate
--- Epithelial plate or epithelial pallium
|
|
|
|
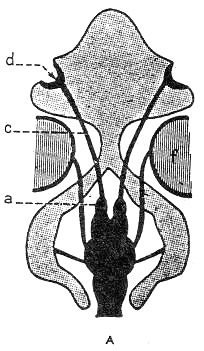
--- Olfactory bulb
--- Directly in front of the corpora striata
|
|
|
|
|
|
a. Salmonid type
--- Majorty of teleosts
--- Olfactory bulb (In front of corpora striata)
------------------------> Nasal capsule
(Olfactory nerve)
b. Cyprinid type
--- Cyprinids\ Silurids\ Gadidae
--- Widely separated from the telencephalon
Directly behind the olfactory organ
--- Extremely short nervus olfactoarius
Long olfactory tract
|
|
|
|
2) Spinal cord ô±âÐ
|
|
|
|
(1) Embryological aspect
--- Neural plate
---> Neural groove
---> Neural canal
<--- Central canal
(2) Anatomical aspect
--- a. Gray matter
--- The center of the spinal cord
--- H \ Upside-down of Y-shape (More frequent in fish)
--- Dorsal\ Ventral horns (Columns\ Ridges)
b. White matter
--- Central nervous pathways
--- Dorsal\ Lateral\ Ventral fasciculus (Bundle of nerve fibres)
c. Central canal
--- Ependyhe barbs or barbels
--- Appendage occurring near the mouth opening
--- Shape/ Length/ Number
--- Species-specific
--- The cod(Gadus morrhua)
The catfish(Ameiurus(Ictarulus) nebulosus)
--- Agonus cataphractus(Perciformes)
Solea lutea(Pleuronectiformes)
--- Generally provided with taste buds and free nerve endings
--- Considered as sensory organs
Generally round/ occasionally oval in cross-section
Sometimes drawn-out at their bases to form wing-like flaps
--- Core of more or less thick cartilagenous rod giving it solidity
--- Attached to a bony element of the skull
Very long barbs usually extending far beyond the body
--- Usually a number of thick nerve strands from the trigeminal nerve(V) or sometimes fibres from the
facial nerve(VII)
ma (Glial cells)
--- "Reissner's thread" in the middle
<--- A secreting product of the subcommissural organ of the diencephalon
--- Ampulla caudalis
--- Longitudinal septum\ Ventral fissure in teleostei
--- Esox lucius (Pike)
--- Separation of dorsal\ ventral fasciculi
--- Generally impossible to separate the white matter from gray matter in teleosts
--- Plates (Roof plate\ Alar plate\ Basal plate\ Floor plate)
--- Strands
--- Thus, plates are not always well-defined
Medulla oblongata
--- Easily observed with large central canal
# Alar plates
--- Interneurons of the sensory roots
Basal plates
--- Motoric nuclei
===> Sulcus limitans (Internus) or His's bordering furrow running between the 2 plates on
each side![]()