![]()
I BACK I RETURN I NEXT I SUMMARY I Any Questions? I
![]()
Cardiovascular system ãýíôâàü»Ðïͧ
|
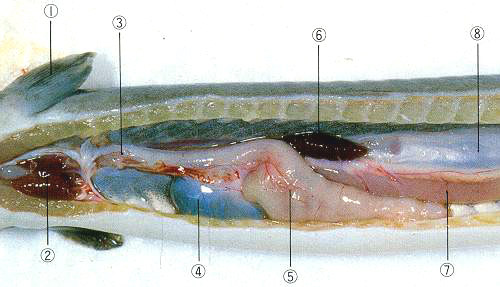
1: Pectoral fin |
|
|
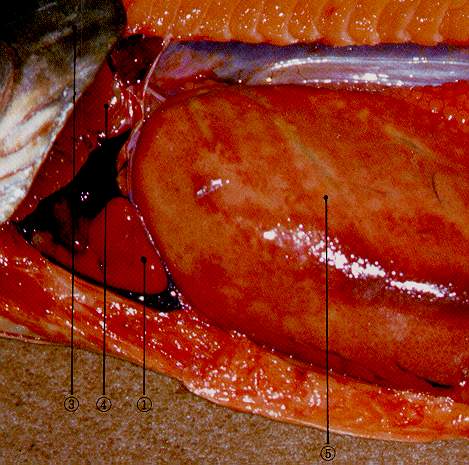
1. Ventricle |
1. Heart
2. Vascular system
--- Arterial and venous system
3. Lymphatic system
--- At present, proved to be absent in fish
Heart ãýíô
--- Protection
--- Cranioventral end of the pectoral girdle
---> Laterally and ventrally surrounding the pericardial cavity
--- Located in the pericardial cavity
--- Location
--- Just posterior to gill and to some extent ventral to gill
Anterior to the abdominal cavity
--- True for all gnathostome fishes
--- but more posteriorly placed in the agnatha
|
|
A left-sided view |
|
|
A dorsal view |
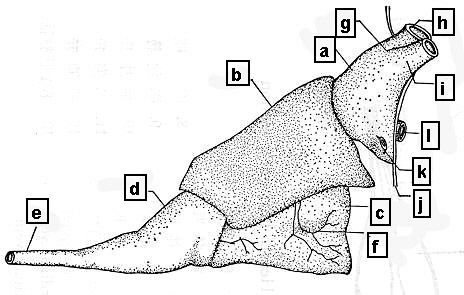
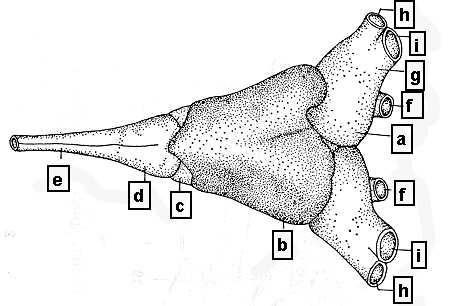
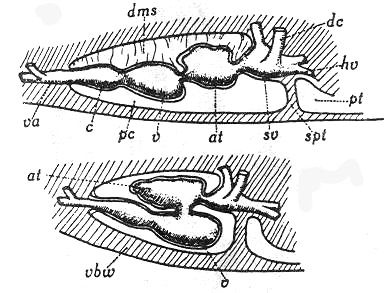
1. Compostion of heart
|
Embryonic stage dc: Cuvier duct, hv: hepatic vein, dms: dorsal mesentry, pt: peritonium, |
|
|
Adult stage |
--- S-shaped structure of the heart
--- The first anlage of the vertebrate heart
--- Lined up in a row of cardiac chambers
--- 4 chambers in a row
--- a. Venous sinus (Sinus venosus)
b. (Cardiac) atrium (Atrium cordis)
c. (Cardiac) ventricle (Ventriculum dordis)
d. Cardiac bulb (Bulbus cordis)
--- Connected to truncus arteriosus
--- Arterial cone (conus arteriosus)
--- Shark, Ray
--- Reduced form in many teleostei
--- Arterial bulb (bulbus arteriosus)
--- Original blood-vessels or its anlage
--- Originated from yolk-sac veins (Vitelline veins, Venae vitellinae)
--- Gubernaculum cordis
--- A ligamentous structure
--- Attaching the tip of the heart to the pericardium
--- Chondrostei\ Teleostei
--- Venous sinus\ cardiac atrium
--- Just widening of the heart tube
Cardia ventricle\ cardiac bulb
--- A thickening of the muscular wall of the heart tube
--- Species variation in carciac anatomy
--- Dipnoi\ Latimeria
--- Partially divided atrium and ventricle
--- 2 symmetrical divisions of each chamber
--- Protopterus (African lungfish)
--- A peculiar kind of A-V valve
--- Consisting of collagenous connective tissue surrounding a cartilagenous core
--- Layers of the heart
--- a. Epicardium with subepicardium
--- Merging into the epithelial lining of the pericardial cavity
b. Myocardium
--- Extremely thin in the sinus venosus
--- Considerable thickness
--- (a) (Cardiac) atrium
(b) Cardiac bulb
(c) Especially in the cardiac ventricle
c. Endocardium with subendocardium
--- Continuous with the corresponding layer in the blood vessels
--- Formation of heart valves
--- Chordae tendinae (A thin tendon thread)
--- Preclusion of the reversion of a valve
1) Venous sinus
--- Location
--- Dorso-caudal region of pericardial cavity
Dorsal to ventricle and aortic bulb
Relatively small compared to the atrium
--- Better developed in teleostei than in the elasmobranchii
--- A very thin layer of heart musculature
--- V wave in ECG
Species variation
--- Associated veins opening into venus sinus
--- By penetration through the transverse septum
(1) Common cardinal veins
--- Bilateral ones
--- Cuvier duct
--- Running down along both sides of esophagus
Dorsal side of venous sinus
# Ductus Cuvieri in the agnatha (Petromyzontes\ Myxini)
A portal heart in the myxini
(2) Hepatic veins
--- Generally posterior wall of the sinus through the penetration of diaphragm
--- Sphincter in the opening in the elasmobranchii
(3) Jugular and subclavian veins
2) Sino-atrial opening and sinoatrial valve (SA valve)
--- Folding both walls of the sinus and atrium
--- At the point where the sinus fuses with the atrial muscle
--- No sinoatrial valve in snakehead
Division of sinoatrial valve into separate portions
--- Eel and sturgeon
3) (Cardiac) atrium
--- Dorsal to ventricle and even the cardiac bulb
--- Thicker than that of the sinus
--- Spongy or trabecular layer of cardiac muscle
--- mm. pectinati
--- Running through the atrial lumen
--- Atrio-ventricular opening (Ostium atrio-ventriculare)
---> Radiation in star-like fashion
---> Branching-out like a fan
---> A muscular net beneath the roof of the atrium
Muscular trabeculae
--- Auriculare
--- Atrial contractions
--- Emptying auriculare of the atrium
--- Cardiac auricle ãýì¼
--- Frequent ventral protrusions of atrium
--- Running along the sides of the ventricles or along the ventral aorta
Coronary sulcus ήßÒϵ
--- Furrow between the atrium and ventricle
--- A portion of nervus vagus (X) and its connective tissue in teleostei
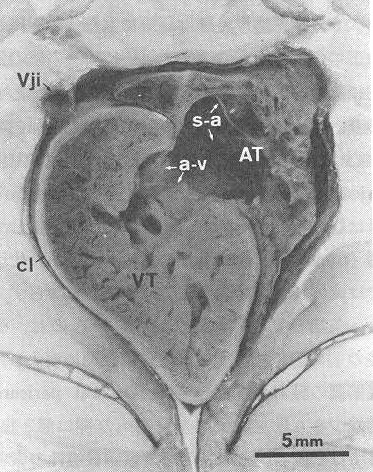
4) Atrio-ventricular opening
|
Atrium and ventricle of carp |
--- Always located in dorsal wall of the ventricle
--- a. Usually 2 equal valves
--- Designated as primary valves
b. Often, a large number of different-sized valves
--- The distance between the AV valve\ the ostium arteriosum(Fig. 185\188)
--- a. Petromyzon
b. Acipencer, esp, salmonidae
--- Bulbo-auricular ridge
5) (Cardiac) ventricles
--- Thicker wall
--- a. Round type
b.Triangular type
--- Active fishes
--- Ventricle in teleostean heart
--- Fitting into the angle between the cleithra
--- A three-sided pyramid
--- a. Spongy layer
--- Most part of ventricle
--- Inner layer of ventricular muscle
b. Compact layer
--- Outer layer of ventricular muscle
--- Distribution of coronary artery
--- Longitudinally, circularly and spirally arranged muscle fibres
--- Correlated with fish activity
--- Absent or developed compact layer
6) Arterial opening
--- Between the cardiac ventricle and cardiac bulb
7) Cardiac bulb ãýíôϹ
--- Species variation
--- Some modification in fishes
No cardiac bulb in the agnatha
--- Arterial cone
--- Original form of cardiac bulb found in shark and ray
--- Separated from the other heart divisions
--- Heart musculature
--- An independant heart-rhythm
--- Many longitudinal rows of valves on internal surface (Fig. 189)
Aortic bulb in many teleosts
--- Regression from cardiac bulb
--- Most anterior part of the heart
--- An elongated barrel
--- Elasmobranchii
Holocephali\ Dipnoi\ Chondrostei\ Holostei
--- Functions of cardiac bulb
--- Maintenence of smooth blood flow leading to prevention of overpressure load to gill
8) Arterial trunk (Ventral aorta) ÔÑØæÊÏ
--- The first portion of the arterial vascular system except for teleostei
--- No heart muscle fibres
Smooth musculature
Arterial or aortic bulb in teleostei
--- The first portion of the arterial system
--- a. Arterial cone in primitive teleosts ÔÑØæêõÞ
--- Myocardium and internal valve
b. Arterial or aortic bulb only in teleostei
--- An onion-shaped swelling of the arterial trunk
--- Organ regressed through arterial cone from cardiac bulb(Conus arteriosus)
--- Enlargement of basal part of ventral aorta
--- Only distal row of valve flaps
--- ie., cardiac bulb
---> Arterial cone
---> Aortic bulb
--- Smooth musculature\ Elastic connective tissue
--- Not rapidly contractible
Absorption of the pressure-wave coming from the ventricle
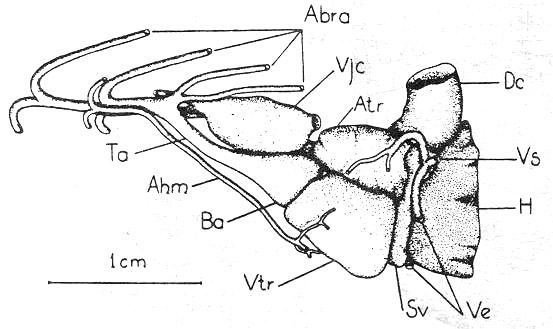
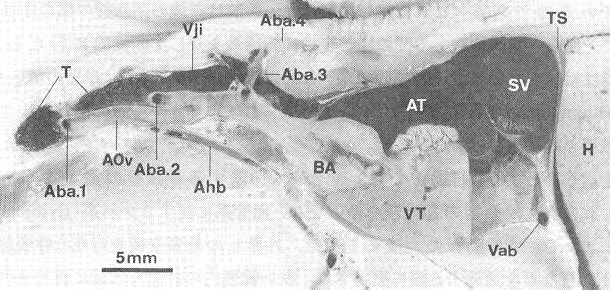
9) Ventral aorta (AOv)
|
T: Thyroid gland, Aba.1 - 4: The first to 4th afferent branchialarteries, Vji: Inferior jugular vein, Ahb: Hypobranchial artery, AOv: Ventral aorta, BA: Aortic bulb, AT: Atrium, VT: Ventricle, SV: Venous sinus, Vab: Abdominal vein, TS: Transverse septum, H: Liver |
10) Pericardial cavity
--- Pharyngeal base
The most anterior part of coelom
Posteriorly, border of pericardial cavity
--- Anterior border of peritoneal cavity
--- Thin coelomic epithelium (Mesothelium)
![]()
Nutrient vessels of the heart
1) Arterial supplies
--- Dorsal aorta\ Last efferent branchial arteries
---> Pericardium
---> Cardiac ligament (ligamenta cordalia)
---> Epicardium of the heart
<--- Coronary arteries
# Coronary arteries in higher vertebrates
2) Venous system
--- Coronary sinus\ Capillary-luminar anstomosis in higher vertebrates
--- Capillary-luminar anstomosis
--- Direct connections between the capillaries and the heart lumen
--- Exception of the bulbus region
(1) Cardiac bulb
--- Anterior cardinal vein
(2) Ventricular wall
--- Pouring into atrial cavity near atrio-ventricular opening (Ostium atrioventriculare)
(3) Atrial wall
--- Pouring into atrial cavity by few veins on the border between the ventricle and the venous sinus
Myogenic excitation
--- Modulation mainly by the adrenergic nervous system
--- Reference book 1-1)
![]()
I BACK I RETURN I NEXT I SUMMARY I Any Questions? I![]()